What Causes Hair Loss (and How to Fight it)
Even though hair loss is often considered to be a male medical issue, people of either gender can suffer from hair loss. The amount of hair loss suffered by a person is often determined by genetics. Genetic hair loss occurs in a pattern that is often referred to as male pattern baldness (MPB) or female pattern baldness (FPB). Androgenetic alopecia, which is the medical name for male pattern baldness, is one of the most common causes of hair loss in patients. Let’s take a look at how genetics influence hair loss as well as other reasons for a loss of hair on the scalp of a person.
Male Pattern Baldness and Female Pattern Baldness Explained
 One of the most common myths about male hair loss is that men inherit the gene that causes balding to occur from the father of their mother. While many people believe this myth, the cause of male pattern baldness is often thought to involve more than one gene (which is also known as being a polygenic trait).
One of the most common myths about male hair loss is that men inherit the gene that causes balding to occur from the father of their mother. While many people believe this myth, the cause of male pattern baldness is often thought to involve more than one gene (which is also known as being a polygenic trait).
It has been documented that people have 23 pairs of chromosomes that contain their genetic information. One pair of these chromosomes, which are known as the “X” and “Y” chromosomes, are what determines the biological sex of a person. When it comes to males and females, women have two “X” chromosomes while men have one “X” chromosome and one “Y” chromosome. In addition, men genetically inherit the “Y” chromosome from their father and the “X” chromosome from their mother.
 The condition known as balding has been found to be greatly associated with the gene found on the “X” chromosome. A study of over 12,000 men with European ancestry reported that people with the gene were found to have more than twice the risk of developing male pattern baldness than people that did not have it.
The condition known as balding has been found to be greatly associated with the gene found on the “X” chromosome. A study of over 12,000 men with European ancestry reported that people with the gene were found to have more than twice the risk of developing male pattern baldness than people that did not have it.
It should be noted that there are 63 other genes that can play a part in the development of male pattern baldness. In addition, only six of these additional 63 genes are found on the “X” chromosome.
On the other hand, the genetic component of female pattern baldness is not as well-known but it is believed that it involves multiple genes (much like male pattern baldness). For example, there are genes that aid in the production of an enzyme known as aromatase (an enzyme that promotes the conversion of an androgen into an estrogen). This might play a part in the development of female pattern baldness and could also be a reason that some women experience a loss of hair after menopause.
Additional Causes for Balding and Hair Loss
In addition to genetics, there are other reasons patients can suffer from hair loss. They include:
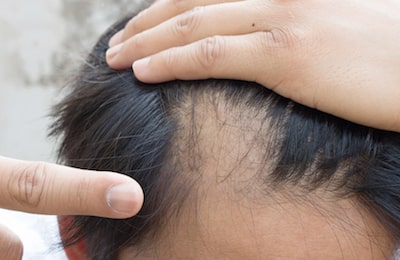 Alopecia Areata (AA) which is an autoimmune disease that can cause hair loss in every part of the skin.
Alopecia Areata (AA) which is an autoimmune disease that can cause hair loss in every part of the skin.- Changes in the hormones of a female that can result from pregnancy or menopause. In addition, men and women can suffer from hair loss that is caused by changes in the level of thyroid hormones.
- Traction Alopecia is the loss of hair caused by the continuous pulling of the hair in a certain section of the scalp. The repetitive pulling of the hair, thanks to hairstyles such as a tight ponytail, can lead to hair loss.
- Large amount of stress, whether it is physical or mental stress, can lead to balding areas on the scalp.
- Trichotillomania is both a hair loss condition and a psychological condition. It is a condition that consists of repeated, but involuntary, hair pulling by a person that result in hair loss in the area impacted by the hair pulling.
- The lack of a proper diet that does not contain essential proteins or nutrients can have a negative impact on the hair growth of a person.
Options to Treat Hair Loss
Topical medication like minoxidil (Rogaine) can often be used to treat the balding areas on the scalp. This topical medication is directly applied to the balding sections on the scalp.
Oral medications like finasteride (Propecia) can be taken by patients on a daily basis to combat male pattern baldness.
Hair transplant surgery, including Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) and Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT), is the process of moving hair follicles from a donor area on the scalp to the balding areas. The hair follicles moved from the donor area are resistant to balding so the results of a hair transplant are permanent.
First Steps to Treating Hair Loss
Anyone that is suffering from hair loss can start the process of treating the condition by scheduling a consultation appointment with a board-certified hair transplant surgeon. The doctor will examine the scalp to determine the cause of the hair loss as well as the medical and surgical options available to a patient. The surgeon will also set realistic expectations so the patient will have a good idea about the type of results that can be expected.
Patients that are interested in learning more about the causes, and treatment, of hair loss are invited to contact our office to schedule a consultation appointment.
MA